Fireside Chat: Exploring the Intersections and Opportunities with Big Data, Precision Medicine, and Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics and Clinical Care
Presented by: Michael Simpson, Joseph Mossel, Leo Grady, Ajit Singh Fireside Chat: Exploring the Intersections and Opportunities with Big Data, Precision Medicine, and Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics and Clinical Care by Michael Simpson, Joseph Mossel, Leo Grady, Ajit Singh https://www.darkdaily.com/wp-content/uploads/Audio%20Files/2024EWC/A-Singh-L-Grady-J-Mossel-M-Simpson-1110-EmpireBCD.mp3 PDF copy of the Presentation Slides...Bringing Artificial Intelligence into Diagnostics and Clinical Practice
Presented by: Leo Grady Bringing Artificial Intelligence into Diagnostics and Clinical Practice by Leo Grady https://www.darkdaily.com/wp-content/uploads/Audio%20Files/2024EWC/L%20Grady%201035%20EmpireBCD.mp3 Session PowerPoint...Boston Children’s Hospital Hires a Prompt Engineer to Help the Healthcare Organization Deploy and Use Artificial Intelligence Applications
This may be a new ‘sign of the times’ as hospitals, clinical laboratories, and other healthcare providers working with AI find they also need to hire their own prompt engineers
Boston Children’s Hospital last year hired a “prompt engineer” to propel the hospital forward in using Artificial intelligence (AI) as part of its business model. But what is AI prompting? It’s a relatively new term and may not be familiar to clinical laboratory and pathology leaders.
AI “prompting,” according to Florida State University, “refers to the process of interacting with an AI system by providing specific instructions or queries to achieve a desired outcome.”
According to workable.com, prompt engineers specialize “in developing, refining, and optimizing AI-generated text prompts to ensure they are accurate, engaging, and relevant for various applications. They also collaborate with different teams to improve the prompt generation process and overall AI system performance.”
Healthcare institutions are getting more serious about using AI to improve daily workflows and clinical care, including in the clinical laboratory and pathology departments. But adopting the new technology can be disruptive. To ensure the implementation goes smoothly, hospitals are now seeking prompt engineers to guide the organization’s strategy for using AI.
When Boston Children’s Hospital leaders set out to find such a person, they looked for an individual who had “a clinical background [and] who knows how to use these tools. Someone who had experience coding for large language models and natural language processing, but who could also understand clinical language,” according to MedPage Today.
“We got many, many applications, some really impressive people, but we were looking for a specific set of skills and background,” John Brownstein, PhD, Chief Innovation Officer at Boston Children’s Hospital and Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Harvard Medical School, told MedPage Today.
“It was not easy to find [someone]—a bit of a unicorn-type candidate,” noted Brownstein, who is also a medical contributor to ABC News.
After a four-month search, the hospital hired Dinesh Rai, MD, emergency room physician and AI engineer, for the position. According to Brownstein, Rai had “actually practiced medicine, lived in a clinical environment,” and had “successfully launched many [AI] applications on top of large language models,” MedPage Today reported.

“Some of the nuances I bring to the table in terms of being a physician and having worked clinically and understanding really deeply the clinical workflows and how we can implement the [AI] technology—where its limits are, where it can excel, and the quickest way to get things [done],” Dinesh Rai, MD (above), told MedPage Today. “I’m happy to be able to help with all of that.” Hospital clinical laboratory and pathology managers may soon by engaging with prompt engineers to ensure the smooth use of AI in their departments. (Photo copyright: LinkedIn.)
Prompt Engineers are like F1 Drivers
“It’s kind of like driving a car, where basically anyone can drive an automatic car, and anyone can go onto ChatGPT, write some text, and get a pretty solid response,” said Rai, describing the act of AI prompting to MedPage today.
Then, there are “people who know how to drive manual, and there are people who will know different prompting techniques, like chain-of-thought or zero-shot prompting,” he added. “Then you have those F1 drivers who are very intimate with the mechanics of their car, and how to use it most optimally.”
The American Hospital Association (AHA) believes that AI “holds great promise in helping healthcare providers gain insights and improve health outcomes.” In an article titled, “How AI Is Improving Diagnostics, Decision-Making and Care,” the AHA noted that, “Although many questions remain regarding its safety, regulation, and impact, the use of AI in clinical care is no longer in its infancy and is expected to experience exponential growth in the coming years.
“AI is improving data processing, identifying patterns, and generating insights that otherwise might elude discovery from a physician’s manual effort. The next five years will be critical for hospitals and health systems to build the infrastructure needed to support AI technology, according to the recently released Futurescan 2023,” the AHA wrote.
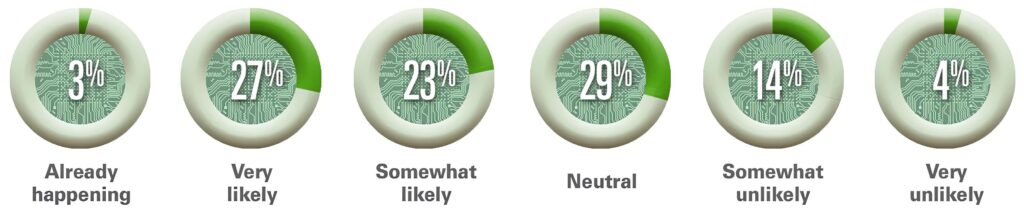
The graphic above is taken from the American Hospital Association’s article about Futurescan’s 2023 survey results on AI in healthcare. “Healthcare executives from across the nation were asked how likely it is that by 2028 a federal regulatory body will determine that Al for clinical care delivery augmentation (e.g., assisted diagnosis and prescription, personalized medication and care) is safe for use by our hospital or health systems,” AHA stated. This would include the use of AI in clinical laboratories and pathology group practices. (Graphic copyright: American Hospital Association.)
The AHA listed the top three opportunities for AI in clinical care as:
- Clinical Decision Tools: “AI algorithms analyze a vast amount of patient data to assist medical professionals in making more informed decisions about care.”
- Diagnostic and Imaging: The use of AI “allows healthcare professionals to structure, index, and leverage diagnostic and imaging data for more accurate diagnoses.”
- Patient Safety: The use of AI improves decision making and optimizes health outcomes by evaluating patient data. “Systems that incorporate AI can improve error detection, stratify patients, and manage drug delivery.”
The hiring of a prompt engineer by Boston Children’s Hospital is another example of how AI is gaining traction in clinical healthcare. According to the Futurescan 2023 survey, nearly half of hospital CEOs and strategy leaders believe that health systems will have the infrastructure in place by 2028 to successfully utilize AI in clinical decision making.
“I’m lucky to [be] in an organization that has recognized the importance of AI as part of the future practice of medicine,” Rai told MedPage Today.
Pathologists and managers of clinical laboratories and genetic testing companies will want to track further advancements in artificial intelligence. At some point, the capabilities of future generations of AI solutions may encourage labs to hire their own prompt engineers.
—JP Schlingman
Related Information:
Why One Hospital Hired an AI Prompt Engineer
This Children’s Hospital is Integrating AI with Healthcare
How Five Healthcare Organizations Are Investing in AI for Patient Care
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
How AI is Improving Diagnostics, Decision-making and Care
Prompt Engineer Job Description
Artificial Intelligence in the Operating Room: Dutch Scientists Develop AI Application That Informs Surgical Decision Making during Cancer Surgery
Speedy DNA sequencing and on-the-spot digital imaging may change the future of anatomic pathology procedures during surgery
Researchers at the Center for Molecular Medicine (CMM) at UMC Utrecht, a leading international university medical center in the Netherlands, have paired artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with DNA sequencing to develop a diagnostic tool cancer surgeons can use during surgeries to determine in minutes—while the patient is still on the operating table—whether they have fully removed all the cancerous tissue.
The method, “involves a computer scanning segments of a tumor’s DNA and alighting on certain chemical modifications that can yield a detailed diagnosis of the type and even subtype of the brain tumor,” according to The New York Times, which added, “That diagnosis, generated during the early stages of an hours-long surgery, can help surgeons decide how aggressively to operate, … In the future, the method may also help steer doctors toward treatments tailored for a specific subtype of tumor.”
This technology has the potential to reduce the need for frozen sections, should additional development and studies confirm that it accurately and reliably shows surgeons that all cancerous cells were fully removed. Many anatomic pathologists would welcome such a development because of the time pressure and stress associated with this procedure. Pathologists know that the patient is still in surgery and the surgeons are waiting for the results of the frozen section. Most pathologists would consider fewer frozen sections—with better patient outcomes—to be an improvement in patient care.
The UMC Utrecht scientist published their findings in the journal Nature titled, “Ultra-Fast Deep-Learned CNS Tumor Classification during Surgery.”

“It’s imperative that the tumor subtype is known at the time of surgery,” Jeroen de Ridder, PhD (above), associate professor in the Center for Molecular Medicine at UMC Utrecht and one of the study leaders, told The New York Times. “What we have now uniquely enabled is to allow this very fine-grained, robust, detailed diagnosis to be performed already during the surgery. It can figure out itself what it’s looking at and make a robust classification,” he added. How this discovery affects the role of anatomic pathologists and pathology laboratories during cancer surgeries remains to be seen. (Photo copyright: UMC Utrecht.)
Rapid DNA Sequencing Impacts Brain Tumor Surgeries
The UMC Utrecht scientists employed Oxford Nanopore’s “real-time DNA sequencing technology to address the challenges posed by central nervous system (CNS) tumors, one of the most lethal type of tumor, especially among children,” according to an Oxford Nanopore news release.
The researchers called their new machine learning AI application the “Sturgeon.”
According to The New York Times, “The new method uses a faster genetic sequencing technique and applies it only to a small slice of the cellular genome, allowing it to return results before a surgeon has started operating on the edges of a tumor.”
Jeroen de Ridder, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Molecular Medicine at UMC Utrecht, told The New York Times that Sturgeon is “powerful enough to deliver a diagnosis with sparse genetic data, akin to someone recognizing an image based on only 1% of its pixels, and from an unknown portion of the image.” Ridder is also a principal investigator at the Oncode Institute, an independent research center in the Netherlands.
The researchers tested Sturgeon during 25 live brain surgeries and compared the results to an anatomic pathologist’s standard method of microscope tissue examination. “The new approach delivered 18 correct diagnoses and failed to reach the needed confidence threshold in the other seven cases. It turned around its diagnoses in less than 90 minutes, the study reported—short enough for it to inform decisions during an operation,” The New York Times reported.
But there were issues. Where the minute samples contain healthy brain tissue, identifying an adequate number of tumor markers could become problematic. Under those conditions, surgeons can ask an anatomic pathologist to “flag the [tissue samples] with the most tumor for sequencing, said PhD candidate Marc Pagès-Gallego, a bioinformatician at UMC Utrecht and a co-author of the study,” The New York Times noted.
“Implementation itself is less straightforward than often suggested,” Sebastian Brandner, MD, a professor of neuropathology at University College London, told The Times. “Sequencing and classifying tumor cells often still required significant expertise in bioinformatics as well as workers who are able to run, troubleshoot, and repair the technology,” he added.
“Brain tumors are also the most well-suited to being classified by the chemical modifications that the new method analyzes; not all cancers can be diagnosed that way,” The Times pointed out.
Thus, the research continues. The new method is being applied to other surgical samples as well. The study authors said other facilities are utilizing the method on their own surgical tissue samples, “suggesting that it can work in other people’s hands.” But more work is needed, The Times reported.
UMC Utrecht Researchers Receive Hanarth Grant
To expand their research into the Sturgeon’s capabilities, the UMC Utrecht research team recently received funds from the Hanarth Fonds, which was founded in 2018 to “promote and enhance the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve the diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of patients with cancer,” according to the organization’s website.
The researchers will investigate ways the Sturgeon AI algorithm can be used to identify tumors of the central nervous system during surgery, a UMC Utrecht news release states. These type of tumors, according to the researchers, are difficult to examine without surgery.
“This poses a challenge for neurosurgeons. They have to operate on a tumor without knowing what type of tumor it is. As a result, there is a chance that the patient will need another operation,” said de Ridder in the news release.
The Sturgeon application solves this problem. It identifies the “exact type of tumor during surgery. This allows the appropriate surgical strategy to be applied immediately,” the news release notes.
The Hanarth funds will enable Jeroen and his team to develop a variant of the Sturgeon that uses “cerebrospinal fluid instead of (part of) the tumor. This will allow the type of tumor to be determined already before surgery. The main challenge is that cerebrospinal fluid contains a mixture of tumor and normal DNA. AI models will be trained to take this into account.”
The UMC Utrecht scientists’ breakthrough is another example of how organizations and research groups are working to shorten time to answer, compared to standard anatomic pathology methods. They are combining developing technologies in ways that achieve these goals.
—Kristin Althea O’Connor
Related Information:
Ultra-fast Deep-Learned CNS Tumor Classification during Surgery
New AI Tool Diagnoses Brain Tumors on the Operating Table
Pediatric Brain Tumor Types Revealed Mid-Surgery with Nanopore Sequencing and AI
AI Speeds Up Identification Brain Tumor Type
Four New Cancer Research Projects at UMC Utrecht Receive Hanarth Grants
Rapid Nanopore Sequencing, Machine Learning Enable Tumor Classification during Surgery



